Category: Domestic Tax
Canadian Tax Filing and Payment Deadlines for Middle-Market Taxpayers for 2024
Executive summary
To simplify your tax-filing experience, we have compiled the key tax filing and payment deadlines for the middle-market taxpayers. This article will serve as a one-stop solution for keeping track of the key tax deadlines approaching. By filing the tax return(s) and paying the taxes due on time, taxpayers can avoid delays to any refund, benefit, or credit payments they may be entitled to. In addition, complying with the due dates will help to avoid late-filing and/or late-payment penalties and interest.
Canadian tax filing and payment deadlines for middle-market taxpayers for 2024
With the approaching tax season, a taxpayer may have to file numerous returns to ensure tax compliance. In addition, with the fast-paced tax developments happening, keeping track of the annual tax filing and payment deadlines could be difficult. This article is a one-stop solution for middle-market taxpayers as it summarizes key tax filing and payment deadlines for the year 2024. The table below is not exhaustive but caters to the most common compliance relevant for middle market taxpayers.
Where the taxpayer omits filing and payment, late files and remits, additional penalties and/or interest kicks in leading to an additional cost burden on the taxpayer.
|
Return/ Form type |
Taxpayer type |
Due date of filing or payment |
|
T1 Returns |
Self-employed individuals or those whose spouses or common-law partners are self-employed |
|
|
Other individuals |
|
|
|
Deceased individuals where the date of death is before Nov. 1, 2023 |
Return due on:
Tax owing due on April 30, 2024 |
|
|
Deceased individuals where the date of death is on or after Nov. 1, 2023 |
|
|
|
Non-residents individuals with a Canadian filing obligation (Section 216/217 returns) |
|
|
|
T2 Corporate tax returns |
For corporations having a Dec. 31, 2023 calendar year-end |
Return due on June 30, 2024* Tax owing due:
|
|
For corporations having a non-calendar year-end |
Return due no later than six months after the end of the corporation’s taxation year Tax owing due:
|
|
|
T3 Trust returns |
Inter-vivos trusts (required to have a calendar year-end) |
Return due 90 days after year-end on March 30, 2024* |
|
Testamentary trusts and Non-resident trusts with a filing obligation in Canada (not required to have a calendar year-end) |
Return due no later than 90 days after the trust’s year-end date |
|
|
T4, T4A-NR, T5 |
– |
Due on Feb. 29, 2024 |
|
NR4 Non-resident information returns |
For an estate or trust |
Return due no later than 90 days after year-end |
|
Other taxpayers |
Return due on March 31, 2024* |
|
|
T5013 Partnership returns |
|
Return due on March 31, 2024* |
|
Where partners are corporate partners (not including professional corporations) |
Return due five months after the end of the taxation year of the partnership |
|
|
All other cases |
Earlier of:
|
|
|
T1134 Information return relating to foreign affiliates |
For individuals and other taxpayers having a Dec. 31, 2023 year-end |
Return due on Oct. 31, 2024 |
|
For other taxpayers with a taxation year beginning in 2023 |
Return due no later than 10 months after the year-end |
|
|
T1135 Foreign income verification statement |
Self-employed individuals or those whose spouses or common-law partners are self-employed |
Return due on June 15, 2024* |
|
Other individuals |
Return due on April 30, 2024 |
|
|
For corporations having a Dec. 31, 2023 calendar year-end |
Return due on June 30, 2024* |
|
|
For corporations with a non-calendar year-end |
Return due no later than six months after the end of the corporation’s taxation year |
|
|
Return due on March 31, 2024* |
|
|
Partnerships where partners are corporate partners (not including professional corporations) |
Return due five months after the end of the taxation year of the partnership |
|
|
All other partnerships |
Earlier of:
|
|
|
Inter-vivos trusts with a Dec. 31, 2023 year-end |
Return due on or before March 30, 2024* |
|
|
Testamentary trusts |
Return due no later than 90 days after the trust’s year-end date |
|
|
T106 Information return of non-arm’s length transactions with non-residents |
Self-employed individuals or those whose spouses or common-law partners are self-employed |
Return due on June 15, 2024* |
|
Other individuals |
Return due on April 30, 2024 |
|
|
For corporations having a Dec. 31, 2023 calendar year-end |
Return due on June 30, 2024* |
|
|
For other corporations |
Return due no later than six months after the end of the corporation’s taxation year |
|
|
Return due on March 31, 2024* |
|
|
Partnerships where partners are corporate partners (not including professional corporations) |
Return due five months after the end of the taxation year of the partnership |
|
|
Inter-vivos trusts with a Dec. 31, 2023 year-end |
Return due on or before March 30, 2024* |
|
|
Testamentary trusts and Non-resident trusts with a filing obligation in Canada |
Return due no later than 90 days after the trust’s year-end date |
|
|
T661 Scientific Research and Experimental Development (SR&ED) claim |
For self-employed individuals |
Form due no later than 12 months after the filing due date of T1 |
|
For corporations (except for non-profit SR&ED corporation) |
Form due no later than 12 months after the filing due date of T2 or 18 months from the end of the taxation year |
|
|
For non-profit SR&ED corporation |
Form due no later than six months after the end of the corporation’s taxation year |
|
|
For partnerships |
Form due no later than 12 months after the earliest of all filing due dates for each member’s income tax return deadline for the tax year in which the partnership’s fiscal period ends. |
|
|
For trusts |
Form due no later than 12 months after the filing due date of T3 |
|
|
RC313 Reportable Uncertain Tax Treatments (RUTT) Information Return |
For corporations having a Dec. 31, 2023 calendar year-end that are required to disclose RUTT |
Information return due no later than June 30, 2024* |
|
For corporations with a non-calendar year-end that are required to disclose RUTT |
Information return due no later than six months after the end of the corporation’s taxation year |
|
|
UHT-2900 Underused Housing Tax Return and Election Form |
Certain taxpayers owning a residential property in Canada |
|
* As per the Canada Revenue Agency (CRA) guidance, when a due date falls on a Saturday, Sunday or public holiday recognized by the CRA, the return is considered filed and the payment is considered to be made on time if the CRA receives the filing, or if the payment or filing is postmarked, on or before the next business day. Therefore, in these instances, as the due date falls on a weekend or a federal holiday, the filing or payment deadline is the first working day following.
This article was written by Farryn Cohn, Chetna Thapar, Mamtha Shree and originally appeared on 2024-02-27. Reprinted with permission from RSM Canada LLP.
© 2024 RSM Canada LLP. All rights reserved. https://rsmcanada.com/insights/tax-alerts/2024/canadian-tax-filing-and-payment-deadlines-for-middle-market-taxpayers-for-2024.html
RSM Canada LLP is a limited liability partnership that provides public accounting services and is the Canadian member firm of RSM International, a global network of independent assurance, tax and consulting firms. RSM Canada Consulting LP is a limited partnership that provides consulting services and is an affiliate of RSM US LLP, a member firm of RSM International. The member firms of RSM International collaborate to provide services to global clients but are separate and distinct legal entities that cannot obligate each other. Each member firm is responsible only for its own acts and omissions, and not those of any other party. Visit rsmcanada.com/about for more information regarding RSM Canada and RSM International.
The information contained herein is general in nature and based on authorities that are subject to change. RSM Canada LLP guarantees neither the accuracy nor completeness of any information and is not responsible for any errors or omissions, or for results obtained by others as a result of reliance upon such information. RSM Canada LLP assumes no obligation to inform the reader of any changes in tax laws or other factors that could affect information contained herein. This publication does not, and is not intended to, provide legal, tax or accounting advice, and readers should consult their tax advisors concerning the application of tax laws to their particular situations. This analysis is not tax advice and is not intended or written to be used, and cannot be used, for purposes of avoiding tax penalties that may be imposed on any taxpayer.
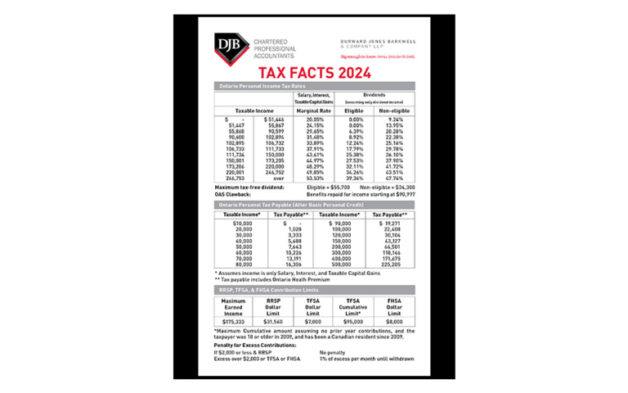
The Tax Free Savings Account
In 2009, the federal government introduced the Tax Free Savings Account (TFSA) to give Canadians another means to save for their financial goals. The TFSA is similar to the Registered Retirement Savings Plan (RRSP) in some ways, but different in others.
TFSA Quick facts:
- Investments grow and compound on a completely tax-free basis within the TFSA.
- Contributions to the TFSA are not tax-deductible, but withdrawals are tax-free and can be made at any time.
- Unused contribution amounts accrue and can be used in future years.
- The current annual contribution limit is $7,000 per person, increasing in $500 increments based on inflation.
- Anyone who was 18 years of age in 2009 and resident in Canada during the period between 2009-2024 and has never contributed to a TFSA has a contribution limit of $95,000.
- Withdrawals from the TFSA do not impact Old Age Security (OAS) benefits.
Things to consider when deciding to use a TFSA:
- Consider how the TFSA fits within your overall financial plan –it may be better to maximize RRSPs, RESPs, or pay down personal debt first.
- The TFSA can complement other retirement savings and since withdrawals are tax-free, they could help you avoid potential Old Age Security (OAS) claw-back.
- Since contributions can be made at any age over 18, a TFSA can be a powerful estate planning tool in building a sizable tax-free asset for an estate or heirs – a benefit similar to using permanent life insurance. If a specific beneficiary is named in a TFSA, the estate administration tax (probate fees) can be avoided on the value of the plan.
- Consider using existing personal non-registered savings to maximize TFSA contribution limits in order to shelter future investment income from tax.
- Investors owning a corporation may want to consider withdrawing additional dividends to fund a TFSA. Although the additional income from the corporation would be taxable, future investment earnings on those contributions would be tax-free.
- Both capital and growth can be withdrawn on a tax-free basis. The total amount withdrawn can then be re-contributed in the next calendar year, or any time afterwards, with no impact on annual contribution limits.
A DJB Wealth Management Advisor can help you make the right choice.
New Trust Reporting: Unexpected Exposure
Breaking news! The CRA will not require bare trusts to file a T3 Income Tax and Information Return (T3 return), including Schedule 15 (Beneficial Ownership Information of a Trust), for the 2023 tax year, unless the CRA makes a direct request.
Changes requiring more trusts (and estates) to file tax returns and more information to be disclosed, first proposed in the 2018 Federal Budget, were delayed several times in the legislative process. As such, many trusts and estates (including many arrangements not commonly considered “trusts”) will be required to file for the first time.
Required reporting has been expanded to include situations where a trust acts as an agent for its beneficiaries (often referred to as a bare trust). This occurs when the person on title or holding the asset is not the true beneficial owner but rather holds the asset for the benefit of another party. There are many common situations that may constitute reportable bare trusts in which no lawyer or written agreement may have ever been involved or drafted. Many parties involved in a bare trust arrangement may not realize that they are, much less that there may be a filing requirement with CRA.
The following lists some examples of potential bare trust arrangements; CRA has not commented on several of the examples below. It is uncertain how they will interpret and enforce the law.
- a child on title of a parent’s home (without the child having beneficial ownership) for probate or estate planning purposes only;
- a parent on title of a child’s property (without the parent having beneficial ownership) to assist the child in obtaining a mortgage;
- one spouse being on title of a house or asset although the other spouse is at least a partial beneficial owner;
- a parent or grandparent holding an investment or bank account in trust for a child or grandchild;
- a corporate bank account opened by the shareholders with the corporation being the beneficial owner of the funds;
- a corporation being on title of an individual’s real estate, vehicle, or other asset, and vice-versa;
- assets registered to one corporation but beneficially owned by a related corporation;
- use of a nominee corporation for real estate development purposes;
- a property management company holding operational bank accounts in trust for their clients, or individuals managing properties for other corporations holding bank accounts for those other corporations; • a lawyer’s specific trust account (while a lawyer’s general trust account would largely be carved out of the filing requirements, a specific trust account would not); and
- a partner of a partnership holding a bank account or asset for the benefit of all the other partners of a partnership.
In addition to bare trust arrangements, other trusts that have not had to file in the past may have a filing obligation under these expanded rules.
Exceptions from filing a return for trusts and bare trust arrangements are available in limited cases. If filing is required, the identity and residency of all the trustees, beneficiaries, settlors, and anyone with the ability (through the terms of the trust or a related agreement) to exert influence over trustee decisions regarding the income or capital of the trust must be disclosed.
Failure to make the required filings and disclosures on time attracts penalties of $25 per day, to a maximum of $2,500, as well as further penalties on any unpaid taxes. New gross negligence penalties may also apply, being the greater of $2,500 and 5% of the highest total fair market value of the trust’s property at any time in the year. These will apply to any person or partnership subject to the new regime.
ACTION ITEM: Consider whether you may have a bare trust arrangement. If so, or if you are unsure, contact us to discuss.
Have you Considered the Scientific Research and Experimental Development Tax Credit?
Is your corporation involved in such activities as agricultural and food processing, information and/or communication technology, life sciences, advanced manufacturing, or independent research to name a few. If so, you may be eligible to claim a Scientific Research and Experimental Development Tax Credit (SRED). When we think of scientific research, we often think of the scientist in the lab wearing a white coat. This isn’t always the case as many claims are a result of development or improvements to a product or process on the shop floor.
In order to qualify, the work must be conducted for the advancement of scientific knowledge or for the purpose of achieving a technological advancement. It is important to note that you do not have to achieve your goal in order to gain new knowledge. For example, if your work allowed you to understand that the idea you tested is not a solution for your situation, this can be considered new knowledge. What’s important is that the knowledge gained advances the understanding of science or technology, not how the work advanced your corporation or business practices.
The work must be a systematic investigation or search that is carried out in a field of science or technology by means of experiment or analysis. A systematic investigation or search refers to how SRED work is carried out. It is more than just having a systematic approach to your work or using established techniques or protocols. A systematic investigation or search must include the following steps:
- Defining a problem.
- Advancing a hypothesis towards resolving that problem.
- Planning and testing the hypothesis by experiment or analysis.
- Developing logical conclusions based on the results.
The federal government will allow corporations to claim an Investment Tax Credit (ITC) of 15% on eligible expenditures. This ITC can be applied against the current year’s income tax or in some cases carried back to a previous tax year or forward to a future tax year. However, some small business corporations may earn an ITC of 35% on eligible expenditures which may be fully refundable in the year.
Eligible expenditures include:
- Canadian wages and salaries.
- An overhead calculation.
- Canadian R&D-related contracts.
- Materials.
- Payments made to eligible research institutions.
The province of Ontario also provides additional incentives to corporations carrying out SRED activities in the province. Certain small business corporations can earn a refundable Ontario Innovation Tax Credit (OITC) of 8% on eligible expenditures. In addition, the Ontario Research and Development Tax Credit (ORDTC) is available. It is a 3.5% non-refundable tax credit based on eligible expenditures incurred by a corporation in a tax year.
It is important to note that the deadline to file a SRED claim on your tax return is eighteen months after your taxation year.
So If you haven’t considered SRED, it may be worthwhile to do so.
Tax Anti-avoidance Rule Changes on the Horizon
Executive summary
The General Anti-Avoidance Rule (GAAR) allows the Canada Revenue Agency (CRA) to assess tax where a taxpayer follows the letter of the law but not its object, spirit, and purpose causing a misuse or abuse of the Income Tax Act (Act). After years of the GAAR provisions remaining mostly unchanged, in the 2023 Budget, the federal government proposed some substantial changes in response to recent jurisprudence and the government’s concern that tax planning was increasingly circumventing the current GAAR.
The amendments, which would broaden the scope of the GAAR, are currently before the House of Commons as part of Bill C-59. Once enacted, the expanded GAAR will apply retroactively to transactions occurring on or after Jan. 1, 2024, except for the penalty which will apply to transactions occurring on or after Royal Assent.
The proposed expanded GAAR appears to reflect Canadian and global tax policy trends around addressing and preventing strategies that exploit perceived loopholes.
Summary of amendments
Preamble – The government proposes to add a preamble to guide the interpretation of the GAAR. It also seeks to clarify that the GAAR is meant to strike a reasonable balance between protecting the tax base, i.e., limiting aggressive tax planning, and taxpayers’ need for certainty in planning their affairs.
Avoidance transaction – For the GAAR to apply, there must be an avoidance transaction. As part of the amendments, the government proposes to capture additional transactions by lowering the threshold to qualify from the “primary purpose” test to “one of the main purposes” test. This lowered threshold now means that if one of the main purposes of the transaction was to obtain a tax benefit and the transaction (or series of transactions of which the transaction is part of) results directly or indirectly in a tax benefit, then it would be an avoidance transaction.
Economic substance – Under the amended rules in Bill C-59, an avoidance transaction that significantly lacks economic substance is an important consideration when determining whether there was a misuse or abuse of the Act.
The factors that may establish that a transaction lacks economic substance are:
- no substantial change in the opportunity for gain or profit and risk of loss of the taxpayer and non-arm’s length persons,
- the expected value of the tax benefit exceeds the expected value of the non-tax economic return, and
- the entire, or almost entire, purpose for undertaking or arranging the transaction or series was to obtain a tax benefit.
This list is non-exhaustive, and the government confirmed that these factors are to be read disjunctively – meaning that not all factors would need to be present to indicate a lack of economic substance. However, if the rationale underlying a provision is to encourage a particular policy, then it could result in a finding that there is no misuse or abuse in appropriate circumstances, for example, utilizing a tax-free savings account.
The economic substance requirement arguably already exists within the current GAAR case law, so it is debatable how much of an impact codifying this rule will have.
Penalty – The government opines that the current GAAR is not a sufficient deterrent to misuse or abuse of the Act as a taxpayer is simply denied the tax benefit. The amendments propose to introduce a penalty of 25% of the tax benefit obtained when the GAAR is found to apply, less any gross negligence penalties. The penalty can be avoided if the taxpayer can demonstrate that at the time the transaction was entered into, they relied on published administrative guidance or court decisions regarding an ‘identical or almost identical’ transaction such that it was reasonable to conclude the GAAR would not apply. This is called the ‘due diligence defence’ and as the CRA notes, it is a very high threshold. The penalty could also be avoided if the transaction was disclosed to the CRA under the mandatory disclosure rules (MDR) either voluntarily, or as required by legislation.
Reassessment period – The CRA normally has three or four years from the date of reassessment to reassess a taxpayer. The GAAR amendments propose a three-year extension to the normal reassessment period for GAAR assessments unless the transaction was disclosed under the MDR.
This article was written by Sigita Bersenas, Mamtha Shree and originally appeared on 2024-02-06. Reprinted with permission from RSM Canada LLP.
© 2024 RSM Canada LLP. All rights reserved. https://rsmcanada.com/insights/tax-alerts/2024/tax-anti-avoidance-rule-changes-on-the-horizon.html
RSM Canada LLP is a limited liability partnership that provides public accounting services and is the Canadian member firm of RSM International, a global network of independent assurance, tax and consulting firms. RSM Canada Consulting LP is a limited partnership that provides consulting services and is an affiliate of RSM US LLP, a member firm of RSM International. The member firms of RSM International collaborate to provide services to global clients but are separate and distinct legal entities that cannot obligate each other. Each member firm is responsible only for its own acts and omissions, and not those of any other party. Visit rsmcanada.com/about for more information regarding RSM Canada and RSM International.
The information contained herein is general in nature and based on authorities that are subject to change. RSM Canada LLP guarantees neither the accuracy nor completeness of any information and is not responsible for any errors or omissions, or for results obtained by others as a result of reliance upon such information. RSM Canada LLP assumes no obligation to inform the reader of any changes in tax laws or other factors that could affect information contained herein. This publication does not, and is not intended to, provide legal, tax or accounting advice, and readers should consult their tax advisors concerning the application of tax laws to their particular situations. This analysis is not tax advice and is not intended or written to be used, and cannot be used, for purposes of avoiding tax penalties that may be imposed on any taxpayer.
AUTOMOBLE DEDUCTION AND BENEFIT RATES: 2024 Limits Released
Various automobile deductions and taxable benefit rates are limited to amounts prescribed by the Department of Finance annually.
On December 18, 2023, the 2024, limits were announced as follows:
The limit on the deduction for non-taxable allowances paid by an employer to an employee using a personal vehicle for business purposes will increase in 2024 by 2 cents to 70 cents/km for the first 5,000 km driven and to 64 cents for each additional km. For Yukon, the Northwest Territories and Nunavut, the tax-exempt allowance will continue to be 4 cents/km higher, which is 74 cents for the first 5,000 km driven and 68 cents for each additional km.
The ceiling on the capital cost for CCA of most passenger vehicles will increase to $37,000 from $36,000, and the limit for zero-emission passenger vehicles will remain at $61,000.
The limit on leasing costs will increase to $1,050/month (from $950/month) for new leases entered into on or after January 1, 2024.
The maximum allowable interest will increase to $350/month (from $300/month) for new loans entered into on or after January 1, 2024.
The general prescribed rate used to determine the taxable benefit relating to the personal portion of automobile operating expenses paid by employers will remain at 33 cents/km. For taxpayers employed principally in selling or leasing automobiles, the rate will remain at 30 cents/km.
ACTION: Compare automobile allowances and other payments made against the limits to determine whether expenditures that do not reduce tax are being made.
Federal Government Denies Expenses on Short-Term Rentals
The Federal government has introduced new proposed measures to disincentivize short-term rentals that aren’t in compliance with their local jurisdiction as of January 1, 2024. This joins other housing affordability legislation like the Underused Housing Tax Act.
The 2023 Federal Economic Statement noted that in the cities of Toronto, Montreal, and Vancouver, there are an estimated 18,900 homes that were being used for short-term rentals (and more than half of Toronto’s short-term rentals are unregistered).
These new measures may result in increased rental income by the taxpayer, making the short-term rental business model less appealing and viable. Read further details in this article, written by RSM Canada.
Employment Insurance: Misconduct
An August 24, 2023, Federal Court of Canada case reviewed whether the taxpayer’s employment had ceased due to misconduct, which would render the taxpayer ineligible for employment insurance. The taxpayer worked at a community health care centre that required all employees to provide proof of full vaccination against COVID-19 unless they provided evidence of a valid medical reason or they had a valid human rights reason (including religion) in accordance with the Ontario Human Rights Code for not being vaccinated. The Social Security Tribunal found that the taxpayer lost his employment due to his own misconduct because he was aware of his employer’s vaccination policy and the consequences of not complying. The Court found that this decision was not unreasonable.
ACTION ITEM: An employee’s cessation of employment due to their failure to comply with the employer’s vaccination policy may result in that individual being ineligible for employment insurance.
REVIVAL OF A CORPORATION: Tax Collection
A June 12, 2023, Court of King’s Bench of Alberta case reviewed CRA’s application to revive a corporation dissolved in 2020. The former sole shareholder opposed the application. The corporation’s capital losses (as quantified during an audit of the 2013 and 2014 years) were used in 2017 and 2018. CRA sought to revive the corporation and issue notices of assessment for 2017 and 2018.
Revival granted
Under the Alberta Business Corporations Act, a creditor has standing to ask that a dissolved corporation be revived. While taxpayers remain liable for tax when income is earned, the liability does not become a debt until taxes are assessed. As no notice of assessment had been issued, CRA had no standing as a creditor. They would only become a creditor if they issued a notice of assessment. This created a circularity issue as an assessment could not be issued to a dissolved corporation. However, the Court has the power to designate someone as an “interested person,” allowing the designated person to revive a dissolved corporation. The Court found that CRA had a valid interest in the revival and sought this remedy to further its interest; that is, to issue a notice of assessment to convert the taxpayer’s liability for taxes into a debt. While the revived corporation would have no assets, no property, no directors, and no shareholders, a dissolved corporation that has been revived is deemed to always have existed. CRA argued that they could pursue the former shareholders on the basis that assets were transferred on dissolution to non-arm’s length parties for less than fair market value consideration. Similar rules are applicable in other provinces.
ACTION ITEM: Dissolving a corporation may not protect former shareholders from CRA taking measures to collect a tax debt.